Have you ever wondered how and when did the Internet start?
The Internet has a vast history. This blog post walks through how the Internet started, the major notable events, and how technology has advanced.
Before starting with history, let us understand the Internet first.
In a nutshell, the Internet is a global network of servers and computers hosting web pages. It allows people to access, share information, and communicate with other users.
Accessing your favorite websites like Google, Twitter, Facebook, Gmail, or any other is accessing the Internet. In addition, sharing information via email, messengers, mobile application, etc., also fall into Internet usage.
In short, most things that consume your mobile data or WiFi are part of the Internet.
Before the Invention of the Modern Internet
The beginning of today’s Internet was not simple. For decades, computer scientists did countless research and put in years of effort to give us our modern World Wide Web.
We have noted some significant developments to walk you through how the Internet started.
- In October 1969, ARPANET became the first network that used packet switching successfully. UCLA and Stanford universities tried transmitting the word Login, but their system crashed on the letter g.
- In 1970, MIT, Harvard University, and BBN deployed ARPANET.
- Raymond Samuel Tomlinson invented email in 1971.
- 1971 started an era of e-books. The thought was to make information from libraries available to users. Declaration of Independence was the first e-book.
- In 1972, France started CYCLADES, a network similar to ARPANET. The project got shut but drew attention to the concept of a host computer responsible for transmitting the data.
- In 1974, TCP/IP was born with a proposal to link networks similar to ARPANET, called inter-network.
- Gary Thuerk, known as the Father of Spam”, launched the first unsolicited commercial email campaign in 1978.
- 1st January 1983 was the deadline for all ARPANET computers to switch to TCP/IP.
- In 1984, domain names got introduced with DNS. Users can access the pages by typing easy-to-remember URLs rather than numeric IPs.
- Tim Berners-Lee proposed the World Wide Web in the year 1989. It was first called Mesh but later renamed the World Wide Web in 1990.
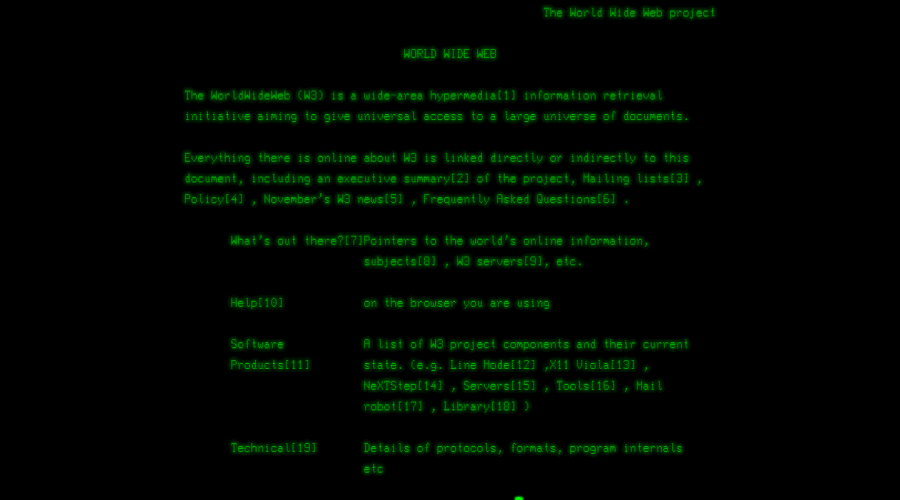
What was the Need, and How the Internet Started?
The concept of the Internet began as ARPANET.
The United States Department of Defense formed the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network (ARPANET). The notion was to have a secure contact medium for the military to remain in contact during the war.
The core purpose was to have a network of Pentagon-funded computers to transmit information during the Cold War. Since ARPANET’s architecture had no hub, losing single or multiple centers during the war did not affect the entire network.
Educational institutions played a significant role and were at the frontline of the research.
Once the war was over, the universities used the advancement in technology as a tool to share information among users.
The importance of the connected network got recognized, and the Internet became famous.
What is the World Wide Web (“www”)?

Many people believe the Internet and the World Wide Web are the same. But there is a slight difference.
The Internet is a global network of computers and servers. It allows users to access and share information with other users.
World Wide Web, in short, “web” or “www,” is a collection of information on these global network computers.
Simply, a web browser uses the Internet to access the web.
What were the Initial Web Browsers?

In 1990, Tim Berners-Lee developed the first web browser WorldWideWeb for the NeXTSTEP operating system. The browser was renamed to Nexus later to avoid confusion with the World Wide Web.
Line Mode Browser was the 2nd in line, the first cross-platform browser compatible with multiple operating systems.
Many other browsers were created in the early 90s, but most were discontinued.
Domains Name, ISP, and Hosting Services
Domain Names
In simple words, a domain name is the address of a website.
At the beginning of the Internet, people used to access web pages on memorable hosts’ numerical IP addresses. For example, an IP address (IPV4) looks like 010.176.982.458.
With the rapid growth of the Internet, it became impossible to maintain the host/website addresses.
So, in 1983, Domain Name System was introduced on the ARPANET and published by the Internet Engineering Task Force.
Instead of typing the IP address, you can call the domain name in a web browser to access a website.
Internet Service Provider (ISP)
An Internet Service Provider (ISP) is a term for an organization that can provide access to the Internet.
The Internet started as a closed network between government agencies, the military, universities, and colleges.
But, with time, these departments began giving their employees Internet access.
The state of accessing the Internet at home became the cause for the creation of ISPs.
It acts as a link between your device and the Internet-connected servers.
At the beginning of the Internet, there were three types of ISPs; Dial-up services , High-speed Internet or Broadband, and DSL (Digital Subscribers Line)
Hosting Services
A hosting service is a web service that facilitates web admins to publish web pages and related data to the Internet.
Hosting services use special computers, called servers, to store the webmaster’s website. This process of storing the data on servers and making the websites available for global users is known as web hosting.
Hosting a website was a costly process initially.
The user must have a dedicated computer or server to transfer data and keep the website accessible to others. The data and web pages were accessible until the devices ran. Data access gets offline whenever those hosts get powered down.
Hosting services began with the launch of GeoCities to overcome this issue in 1994. However, initially, the hosting services were not accessible to everyone.
But things have evolved. Hosting services are now available for individuals and groups without any restrictions.
Also read: How to Design a Website That Drives Leads and Sales
The Need for Search Engines

With time the number of websites increased.
The father of the Internet, Tim Berners-Lee, created the first directory in 1992. The concept was to help users navigate and find relevant websites. Later in 1995, other directories like Yahoo, DMOZ, The Starting Point Directory, etc., were launched.
There was a surge in the number of websites between 1995 and 2000. As a result, the directories had their golden era during this tenure.
With websites populating the directories, it became difficult to find the right websites.
The concept of a search engine came into existence to search for websites within directories. Users can browse as well as search for the websites.
Yahoo launched its search engine in March 1995. Later in 1996, Larry Page and Sergey Brin launched their search engine BackRub. The new search engine showed website results based on its backlink analysis. BackRub later became Google, the biggest search engine to date, with nearly 85% desktop search share and around 96% mobile search share.
What is a Search Engine?
A search engine is a program that crawls the whole web, saves details in its index, and provides valuable results from the web for user queries.
It tends to lead users to relevant information on high-quality websites. A search engine filters the wealth of data available on the web for user searches.
In short, it allows users to find websites with ease.
Search engines use modern algorithms to determine the quality of the website’s pages. For example, Google uses 200+ signals to analyze website quality for ranking.
It assigns every page value in its index for relevant search phrases. Then, when a user queries, the search engine shows the website listing from its index.
As per Statcounter (Mar 2023), below is the sequence of the top 6 search engines as per their popularity:
- Bing
- Yahoo
- Yandex
- Baidu
- DuckDuckGo
How has the Internet Evolved over the Years?

Evolution is inevitable over time, and it’s no different for the Internet.Over the past three decades, the Internet has evolved on many levels. Everything contributes to the remarkable growth of the Internet, from sending text emails to conference calls and basic text web pages to progressive web applications.
The Internet has become a need of the hour for everyone in the 21st century.
It’s not limited to computers; it has reached mobile phones, wearables, smart homes, automobiles, AI, ML, and more. Likewise, it’s not limited to sharing information but has become a part of life.
The Internet entertains, communicates, transacts, and keeps you updated with the latest information across the globe.
What is the importance of the Internet in daily life?
As per Statista (Jan 2023), we have 5.16 billion Internet users who use the service in one way or another. The Internet has brought knowledge to your fingertips. Below are some scenarios where the Internet has transformed your daily life:
- Online banking has enabled bank services on your mobile/computer. You can transfer money, get your statement, or start any investment anywhere.
- E-commerce allows selling and purchasing goods and services at your doorstep at competitive pricing.
- Online services have changed how people book appointments, study, enjoy sports, plan travel, and more.
- Communication, the core purpose of the beginning of the Internet, became one of the most common means of internet consumption.
- The entertainment industry has flourished. Platforms like YouTube, Netflix, and Amazon Prime have tons of content for users and content producers to monetize.
Do you have an idea as big as the Internet? Or something to monetize from it? We help businesses digitize and monetize it, you can connect with us for a free consultation on digital growth.



2 Responses
Like!! Thank you for publishing this awesome article.
Like!! Thank you for publishing this awesome article.